PROTECTED SOURCE SCRIPT
Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table)
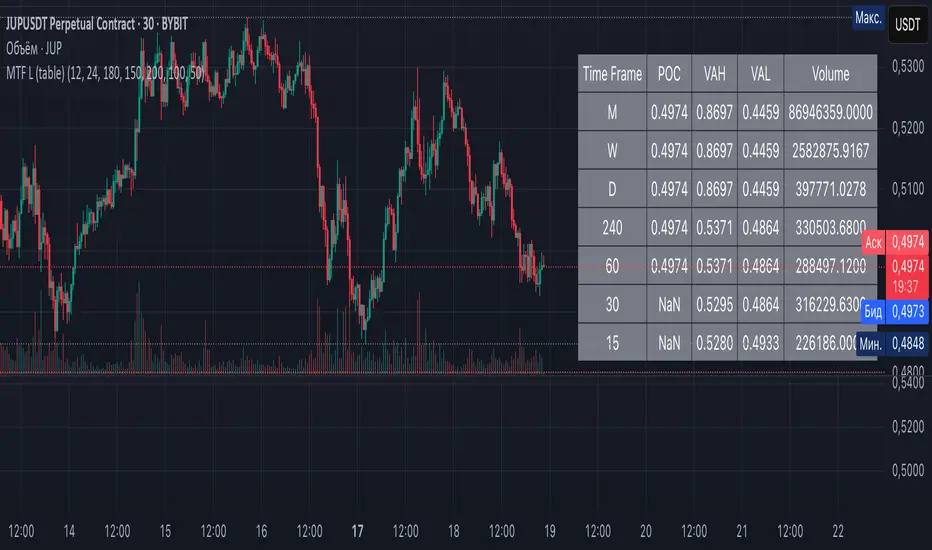
Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) Indicator: Functionality and Uses
Overview: The Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) indicator is a technical analysis tool that highlights key volume-based support and resistance levels across multiple timeframes. It leverages volume profile concepts – specifically the Point of Control (POC) and Value Area High/Low (VAH/VAL) – to identify “liquidity zones” where trading activity was heaviest . Unlike a standard single-timeframe volume profile, this indicator compiles data from several timeframes (e.g. monthly, weekly, daily, intraday) and displays the results in a convenient table format on the chart. The goal is to give traders a consolidated view of important price levels (derived from volume concentrations) across different horizons, helping them plan trades with a broader market perspective.
Purpose and Functionality of the Indicator
Multi-Timeframe Analysis: The primary objective of this indicator is to simplify multi-timeframe analysis of volume distribution. Rather than manually checking volume profiles on separate charts for each timeframe, the tool automatically calculates the key levels for each selected timeframe and presents them together. This includes higher-level perspectives (like monthly or weekly volume hotspots) alongside shorter-term levels (daily or hourly), ensuring that traders don’t miss significant zones from any timeframe . By offering a broader perspective on support and resistance levels, multi-timeframe tools help improve risk management and signal confirmation , and this indicator is designed to provide that volume-based perspective at a glance.
Table Format Display: Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) specifically presents the information as a table (as opposed to plotting lines on the chart). Each row in the table typically corresponds to a timeframe (for example, Monthly, Weekly, Daily, 4H, 1H, 30M, 15M), and the columns list the calculated POC, VAH, VAL, and possibly the average volume for that timeframe’s look-back period. By structuring the data in a table, traders can quickly read off the exact price levels of these liquidity zones without having to visually trace lines. This format makes it easy to compare levels across timeframes or note where multiple timeframes’ levels cluster near the same price – a sign of especially strong support/resistance. The indicator uses a user-defined number of bars or length of history for each timeframe to calculate these values (so you can adjust how far back it looks to define the volume profile for each period).
Objective: In summary, the functionality is geared toward identifying high-liquidity price zones across multiple time scales and presenting them clearly. These high-liquidity zones often coincide with areas where price reacts (stalls, reverses, or accelerates) because a lot of trading activity (hence, orders and volume) took place there in the past. The indicator’s objective is to alert the trader to those areas in advance. It effectively answers questions like: “Where are the major volume concentration levels on the 1-hour, daily, and weekly charts right now?” and “Are there overlapping volume-based support/resistance levels from different timeframes around the current price?” By compiling this information, the indicator helps traders incorporate context from multiple timeframes in their decision-making, without needing to flip through numerous charts.
Identifying Liquidity Zones with POC, VAH, and VAL
Liquidity Zones Defined: In market terms, a “liquidity zone” is an area of the chart where a significant amount of trading occurred, meaning high liquidity (many buyers and sellers exchanged volume there). These zones often act as support or resistance because past heavy trading indicates consensus or interest around those price levels. This indicator identifies liquidity zones through volume profile analysis on each timeframe’s recent price action. Essentially, it looks at the distribution of trading volume at different prices over the specified period and finds the value area – the range of prices that encompassed the majority of that volume (commonly around 70% of the total volume ). Within that value area, it pinpoints the Point of Control (POC), which is the single price level that had the highest traded volume (the peak of the volume profile) . The upper and lower boundaries of that high-volume range are marked as Value Area High (VAH) and Value Area Low (VAL) respectively . Together, the VAH and VAL define the liquidity zone where the market spent most of its time and volume, and POC highlights the most traded price in that zone.
• Point of Control (POC): The POC is the price level with the greatest volume traded for the given period. It represents the price at which the most liquidity was exchanged – effectively the market’s “center of gravity” for that timeframe’s trading activity . The indicator calculates the POC for each selected timeframe by scanning the volume at each price; the price with maximum volume is flagged as that timeframe’s POC. In the table, the POC might be highlighted or listed as a key level (sometimes traders color-code it or mark it for emphasis). Because so many positions were opened or closed at the POC, it often serves as a strong support/resistance. For example, if price falls to a major POC from above, traders expect buyers may step in there (since it was a popular buy/sell level historically), potentially causing a bounce. Conversely, if price breaks through a POC decisively, it may signal a significant shift in market acceptance.
• Value Area High (VAH) and Low (VAL): The VAH and VAL are the price boundaries of the value area, which is typically defined to contain about 70% of the total traded volume for the period . In other words, between VAH and VAL is where the “bulk” of trading occurred, and outside this range is where relatively less volume traded. The indicator derives VAH/VAL by accumulating volume from the highest-volume price (POC) outward until ~70% of volume is covered (this is a common method for volume profile value area). VAH is the top of this high-volume region and VAL is the bottom. These levels are important because they often act like support/resistance boundaries: when price is inside the value area, it’s in a high-liquidity zone and tends to oscillate between VAH and VAL; when price moves above VAH or below VAL, it’s leaving the high-volume zone, which can indicate a potential trend or imbalance (price entering a lower-liquidity area where it might move faster until finding the next liquidity zone). Traders watch VAH/VAL for signs of rejection or acceptance: for instance, a price rally that falters at VAH suggests that level is acting as resistance (sellers defending that high-volume area), whereas if price pushes above VAH, it may continue until the next timeframe’s zone or until it finds new interest. The Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 indicator gives the VAH and VAL for each timeframe, essentially mapping out the upper and lower bounds of key liquidity zones at those scales.
How the Indicator Identifies These: Under the hood, the indicator likely uses historical price and volume data for each timeframe’s lookback window. For each timeframe (say the last 20 weekly bars for a weekly profile, last 100 daily bars for a daily profile, etc.), it constructs a volume profile (a histogram of volume at each price). From that distribution, it finds the POC (highest volume bin) and calculates VAH/VAL around it. The output is a set of numbers (price levels) that mark where those zones lie. In practice, if using the Lines version of this indicator, those levels are drawn as horizontal lines on the chart and labeled by timeframe (e.g., a line at 1.2345 labeled “D POC” for Daily POC) . In the Table version, those values are instead listed in text form. Either way, the identification process is the same – it’s finding the high-volume price regions on each timeframe and calling them out. By doing this for multiple timeframes concurrently, the indicator reveals how these liquidity zones from different periods relate to each other. For example, you might discover that a daily-chart value area overlaps with a weekly-chart POC, creating a particularly strong zone of interest. This kind of insight is hard to get from a single timeframe analysis alone.
Volume Profile Data Across Multiple Timeframes
Multiple Timeframes in One View: One of the biggest advantages of this indicator is the ability to see volume profile information from various timeframes side by side. Traders often perform multiple timeframe analysis to get a fuller picture — for instance, checking monthly or weekly levels for long-term context while planning a trade on a 4-hour chart. This indicator automates that process for volume-based levels. The table will typically list each chosen timeframe (which could be preset or user-selected). For each timeframe, you get the POC, VAH, VAL, and possibly an average volume metric. The “average volume” likely refers to the average volume per bar or the average volume traded over the profile’s duration for that timeframe, which gives a sense of how significant that period’s activity is. For example, a weekly profile might show an average volume of say 500k per week, versus a daily profile average of 80k per day – indicating the scale of trading on weekly vs daily. High average volume on a timeframe means its liquidity zones were formed with a lot of participation, possibly making them more reliable support/resistance. By comparing these, traders can gauge which timeframes had unusually high or low activity recently. The table format makes such comparisons straightforward.
Identification of Confluence: Because all the data is presented together, traders can quickly spot confluence or overlaps between timeframes. If two different timeframes show liquidity zones at similar price levels, that price becomes extremely noteworthy. For instance, suppose the indicator shows: a 1-hour POC at 1.1300, a 4-hour VAL at 1.1280, and a daily VAL at 1.1290. These are all in a tight range – effectively indicating a multi-timeframe liquidity zone around 1.1280–1.1300. A trader seeing this cluster in the table will recognize that as a strong support area, since multiple profiles from intraday to daily all suggest heavy trading interest there. Similarly, overlaps of VAH (resistance zone) from different timeframes could signal a strong ceiling. The multi-timeframe view prevents a trader from, say, going long into a major weekly POC above, or shorting when there’s a huge monthly value-area low just below – situations where awareness of higher timeframe volume structure can make the difference between a good and bad trade.
User Customization: The indicator is flexible in that you can typically adjust which timeframes to include and how many bars to use for each timeframe’s calculation. For example, one might configure it to calculate monthly levels using the past 12 monthly bars (1 year of data), weekly levels using the past 20 weeks, daily using 100 days, etc., depending on preference. By tuning the “bars count” or period length , the trader can focus on recent liquidity zones or incorporate more history if desired. Shorter lookback might catch more recent shifts in volume distribution (important if the market structure changed recently), while longer lookback gives more established levels. This customization ensures the indicator’s output can be tailored to different trading styles (short-term vs swing vs long-term investing). Regardless of settings, the multi-timeframe table allows simultaneous visibility of the chosen timeframes’ volume landscape. This comprehensive view is the core strength: it consolidates data that normally requires flipping through multiple charts.
Using the Liquidity Zones Data for Trading Decisions
Traders can use the information from the MTF Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) indicator in several practical ways to enhance their decision-making:
• Identify Support and Resistance: Each liquidity zone acts as a potential support or resistance area. For example, if the table shows a daily VAH at a certain level above the current price, that level might serve as resistance if the price rallies up to it (since it marks the top of a high-volume region where sellers might step in). Conversely, a weekly VAL below current price could act as support on a dip. By noting these levels in the table, a trader planning an entry or exit can anticipate where the price might stall or reverse. Essentially, you get a map of high-interest price levels from different timeframes, which you can mark on your trading chart for guidance.
• Plan Entries and Exits Around Key Levels: Many traders incorporate volume profile levels into their strategies, for instance: buying near VAL (betting that the value area will hold and price will revert upward), or selling/shorting near VAH (expecting the top of value to hold as resistance), or trading breakouts when price moves outside the value area. With the multi-timeframe table, one can refine these tactics by also considering higher timeframe levels. Suppose you see that on the 1-hour chart the price is just above its 1H POC, but the table indicates that just slightly above, there’s also the daily POC. You might delay a long entry until price clears that daily POC, because that could be a stronger intraday barrier. Or if you intend to take profit on a long trade, you might choose a target just below a weekly VAH since price may struggle to climb past that on the first attempt. The indicator thus acts as a guide for precision in entry/exit decisions, aligning them with where liquidity is high.
• Gauge Trend Strength and Directional Bias: By observing where current price is relative to these volume zones, traders can infer certain market conditions. For instance, if price is trading above the VAH of multiple timeframes’ value areas, it suggests the market is in a more bullish or overextended territory (price accepted above prior value), whereas if price is below multiple VALs, it’s in bearish or undervalued territory relative to recent history. If the price stays around a POC, it indicates consolidation or equilibrium (market comfortable at that price). Traders can use this context for bias – e.g., if price is above the weekly VAH, you might lean bullish but watch for potential pullbacks to that VAH level (now a support). If price is below the monthly VAL, you might avoid longs until it re-enters that value area. In essence, the liquidity zones provide context of value vs. price: is price trading within the high-volume areas (implying range-bound behavior) or outside them (implying a breakout or trending move)? This can prevent chasing trades at poor locations.
• Combine with Other Indicators/Analysis: It’s generally advised to not use any single indicator in isolation, and this holds true here. The liquidity zones from this indicator are best used alongside price action or other technical signals for confirmation . For example, if a bullish candlestick reversal pattern forms right at a confluence of a 4H VAL and Daily POC, that’s a stronger buy signal than the pattern alone. Or if an oscillator shows overbought exactly as price hits a weekly VAH, it adds conviction to a possible short. The indicator’s table basically gives you a shortlist of critical price levels; you can then watch how price behaves at those levels (via candlesticks, order flow, etc.) to make the final trade decision. Traders might set alerts for when price approaches one of the listed levels, or they might drop down to a lower timeframe to fine-tune an entry once a key zone is reached. By integrating this volume-based insight with trend analysis, chart patterns, or momentum indicators, one can make more informed and high-probability decisions rather than trading in the dark.
• Risk Management and Stop Placement: High-liquidity zones can also inform stop-loss placement. Ideally, you want your stop on the other side of a strong support/resistance. If you go long near a VAL, you might place your stop just below the VAL (since a move beyond that suggests the high-volume zone didn’t hold). If you short near a VAH, a stop just above the VAH or POC could be logical. Moreover, if multiple timeframes show overlapping zones, a stop beyond all of them could be even safer (albeit at the cost of a wider stop). The indicator helps identify those spots. It also warns you of where not to put a stop – for example, placing a stop-loss right at a POC might be unwise because price could gravitate to that POC repeatedly (due to its magnetic effect as a high-volume price). Instead, a trader might choose a stop beyond the far side of the value area. By using the table’s information, you can align your risk management with areas of high liquidity, reducing the chance of being whipsawed by normal volatility around heavily traded levels .
Benefits of the Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones Indicator
Using the Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) indicator offers several key benefits for traders, ultimately aiming to streamline analysis and improve decision quality:
• Consolidated Key Levels: It provides a clear, consolidated view of crucial volume-driven levels from multiple timeframes all at once . This saves time and ensures you always account for major support/resistance zones that come from higher or lower timeframe volume clusters. You won’t accidentally overlook a significant weekly level while focused on a 15-minute chart, for example.
• Enhanced Multi-Timeframe Insight: By aligning information from long-term and short-term periods, the indicator helps traders see the “bigger picture” while still operating on their preferred timeframe. This multi-scale awareness can improve trade timing and confidence. You’re effectively doing multi-timeframe analysis with volume profiles in an efficient manner, which can confirm or caution your trade ideas (e.g., a trend looks strong on the 1H, but the table shows a huge monthly VAH just overhead – a reason to be cautious or take profit early).
• Improved Decision Making and Precision: Knowing where liquidity zones lie allows for more precise entries, exits, and stop placements. Traders can make informed decisions such as waiting for a pullback to a value area before entering, or taking profits before price hits a major POC from a higher timeframe. These decisions are grounded in objectively important price levels, potentially leading to higher probability trades and better risk-reward setups. It essentially enhances your strategy by adding a layer of volume context – you’re trading with an awareness of where the market’s interest is heaviest.
• Volume-Based Confirmation: Price alone can sometimes be deceptive, but volume tells the true story of participation. The liquidity zones indicator provides volume-based confirmation of support/resistance. If a price level is identified by this tool, it’s because significant volume happened there – adding weight to that level’s importance. This can help filter out false support/resistance levels that aren’t backed by volume. In other words, it highlights high-quality levels that many traders (and possibly institutions) have shown interest in.
• Adaptable to Different Trading Styles: Whether one is a scalper looking at intraday (15M, 5M charts) or a swing trader focusing on daily/weekly, the indicator can be configured to those needs. You choose which timeframes and how much data to consider. This means the concept of liquidity zones can be applied universally – from spotting intraday pivot levels with volume, to seeing long-term value zones on an investment. The consistent methodology of POC/VAH/VAL across scales provides a common framework to analyze any market and timeframe.
• Informed Risk Management: As discussed, the knowledge of multi-timeframe volume zones aids in risk management. By placing stops beyond major liquidity areas or avoiding trades that run into strong volume walls, traders can reduce the likelihood of whipsaw losses. It’s an extra layer of defense to ensure your trade plan accounts for where the market has historically found lots of interest (hence likely friction). This level of informed planning can be the difference between a well-managed trade and an avoidable loss.
In conclusion, the Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) indicator serves as a powerful analytical aid, giving traders a structured view of where price is likely to encounter support or resistance based on volume concentrations across timeframes. Its functionality centers on identifying those liquidity zones (via POC, VAH, VAL) and presenting them in an easy-to-read format, while its ultimate purpose is to help traders make more informed decisions. By integrating this tool into their workflow, traders can more confidently navigate price action, knowing the objective volume-based landmarks that lie ahead. Remember that while these volume levels often coincide with strong S/R zones, it’s best to use them in conjunction with other technical or fundamental analysis for confirmation . When used appropriately, the indicator can streamline multi-timeframe analysis and enhance your overall trading strategy , giving you an edge in identifying where the market’s liquidity (and opportunity) resides.
Overview: The Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) indicator is a technical analysis tool that highlights key volume-based support and resistance levels across multiple timeframes. It leverages volume profile concepts – specifically the Point of Control (POC) and Value Area High/Low (VAH/VAL) – to identify “liquidity zones” where trading activity was heaviest . Unlike a standard single-timeframe volume profile, this indicator compiles data from several timeframes (e.g. monthly, weekly, daily, intraday) and displays the results in a convenient table format on the chart. The goal is to give traders a consolidated view of important price levels (derived from volume concentrations) across different horizons, helping them plan trades with a broader market perspective.
Purpose and Functionality of the Indicator
Multi-Timeframe Analysis: The primary objective of this indicator is to simplify multi-timeframe analysis of volume distribution. Rather than manually checking volume profiles on separate charts for each timeframe, the tool automatically calculates the key levels for each selected timeframe and presents them together. This includes higher-level perspectives (like monthly or weekly volume hotspots) alongside shorter-term levels (daily or hourly), ensuring that traders don’t miss significant zones from any timeframe . By offering a broader perspective on support and resistance levels, multi-timeframe tools help improve risk management and signal confirmation , and this indicator is designed to provide that volume-based perspective at a glance.
Table Format Display: Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) specifically presents the information as a table (as opposed to plotting lines on the chart). Each row in the table typically corresponds to a timeframe (for example, Monthly, Weekly, Daily, 4H, 1H, 30M, 15M), and the columns list the calculated POC, VAH, VAL, and possibly the average volume for that timeframe’s look-back period. By structuring the data in a table, traders can quickly read off the exact price levels of these liquidity zones without having to visually trace lines. This format makes it easy to compare levels across timeframes or note where multiple timeframes’ levels cluster near the same price – a sign of especially strong support/resistance. The indicator uses a user-defined number of bars or length of history for each timeframe to calculate these values (so you can adjust how far back it looks to define the volume profile for each period).
Objective: In summary, the functionality is geared toward identifying high-liquidity price zones across multiple time scales and presenting them clearly. These high-liquidity zones often coincide with areas where price reacts (stalls, reverses, or accelerates) because a lot of trading activity (hence, orders and volume) took place there in the past. The indicator’s objective is to alert the trader to those areas in advance. It effectively answers questions like: “Where are the major volume concentration levels on the 1-hour, daily, and weekly charts right now?” and “Are there overlapping volume-based support/resistance levels from different timeframes around the current price?” By compiling this information, the indicator helps traders incorporate context from multiple timeframes in their decision-making, without needing to flip through numerous charts.
Identifying Liquidity Zones with POC, VAH, and VAL
Liquidity Zones Defined: In market terms, a “liquidity zone” is an area of the chart where a significant amount of trading occurred, meaning high liquidity (many buyers and sellers exchanged volume there). These zones often act as support or resistance because past heavy trading indicates consensus or interest around those price levels. This indicator identifies liquidity zones through volume profile analysis on each timeframe’s recent price action. Essentially, it looks at the distribution of trading volume at different prices over the specified period and finds the value area – the range of prices that encompassed the majority of that volume (commonly around 70% of the total volume ). Within that value area, it pinpoints the Point of Control (POC), which is the single price level that had the highest traded volume (the peak of the volume profile) . The upper and lower boundaries of that high-volume range are marked as Value Area High (VAH) and Value Area Low (VAL) respectively . Together, the VAH and VAL define the liquidity zone where the market spent most of its time and volume, and POC highlights the most traded price in that zone.
• Point of Control (POC): The POC is the price level with the greatest volume traded for the given period. It represents the price at which the most liquidity was exchanged – effectively the market’s “center of gravity” for that timeframe’s trading activity . The indicator calculates the POC for each selected timeframe by scanning the volume at each price; the price with maximum volume is flagged as that timeframe’s POC. In the table, the POC might be highlighted or listed as a key level (sometimes traders color-code it or mark it for emphasis). Because so many positions were opened or closed at the POC, it often serves as a strong support/resistance. For example, if price falls to a major POC from above, traders expect buyers may step in there (since it was a popular buy/sell level historically), potentially causing a bounce. Conversely, if price breaks through a POC decisively, it may signal a significant shift in market acceptance.
• Value Area High (VAH) and Low (VAL): The VAH and VAL are the price boundaries of the value area, which is typically defined to contain about 70% of the total traded volume for the period . In other words, between VAH and VAL is where the “bulk” of trading occurred, and outside this range is where relatively less volume traded. The indicator derives VAH/VAL by accumulating volume from the highest-volume price (POC) outward until ~70% of volume is covered (this is a common method for volume profile value area). VAH is the top of this high-volume region and VAL is the bottom. These levels are important because they often act like support/resistance boundaries: when price is inside the value area, it’s in a high-liquidity zone and tends to oscillate between VAH and VAL; when price moves above VAH or below VAL, it’s leaving the high-volume zone, which can indicate a potential trend or imbalance (price entering a lower-liquidity area where it might move faster until finding the next liquidity zone). Traders watch VAH/VAL for signs of rejection or acceptance: for instance, a price rally that falters at VAH suggests that level is acting as resistance (sellers defending that high-volume area), whereas if price pushes above VAH, it may continue until the next timeframe’s zone or until it finds new interest. The Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 indicator gives the VAH and VAL for each timeframe, essentially mapping out the upper and lower bounds of key liquidity zones at those scales.
How the Indicator Identifies These: Under the hood, the indicator likely uses historical price and volume data for each timeframe’s lookback window. For each timeframe (say the last 20 weekly bars for a weekly profile, last 100 daily bars for a daily profile, etc.), it constructs a volume profile (a histogram of volume at each price). From that distribution, it finds the POC (highest volume bin) and calculates VAH/VAL around it. The output is a set of numbers (price levels) that mark where those zones lie. In practice, if using the Lines version of this indicator, those levels are drawn as horizontal lines on the chart and labeled by timeframe (e.g., a line at 1.2345 labeled “D POC” for Daily POC) . In the Table version, those values are instead listed in text form. Either way, the identification process is the same – it’s finding the high-volume price regions on each timeframe and calling them out. By doing this for multiple timeframes concurrently, the indicator reveals how these liquidity zones from different periods relate to each other. For example, you might discover that a daily-chart value area overlaps with a weekly-chart POC, creating a particularly strong zone of interest. This kind of insight is hard to get from a single timeframe analysis alone.
Volume Profile Data Across Multiple Timeframes
Multiple Timeframes in One View: One of the biggest advantages of this indicator is the ability to see volume profile information from various timeframes side by side. Traders often perform multiple timeframe analysis to get a fuller picture — for instance, checking monthly or weekly levels for long-term context while planning a trade on a 4-hour chart. This indicator automates that process for volume-based levels. The table will typically list each chosen timeframe (which could be preset or user-selected). For each timeframe, you get the POC, VAH, VAL, and possibly an average volume metric. The “average volume” likely refers to the average volume per bar or the average volume traded over the profile’s duration for that timeframe, which gives a sense of how significant that period’s activity is. For example, a weekly profile might show an average volume of say 500k per week, versus a daily profile average of 80k per day – indicating the scale of trading on weekly vs daily. High average volume on a timeframe means its liquidity zones were formed with a lot of participation, possibly making them more reliable support/resistance. By comparing these, traders can gauge which timeframes had unusually high or low activity recently. The table format makes such comparisons straightforward.
Identification of Confluence: Because all the data is presented together, traders can quickly spot confluence or overlaps between timeframes. If two different timeframes show liquidity zones at similar price levels, that price becomes extremely noteworthy. For instance, suppose the indicator shows: a 1-hour POC at 1.1300, a 4-hour VAL at 1.1280, and a daily VAL at 1.1290. These are all in a tight range – effectively indicating a multi-timeframe liquidity zone around 1.1280–1.1300. A trader seeing this cluster in the table will recognize that as a strong support area, since multiple profiles from intraday to daily all suggest heavy trading interest there. Similarly, overlaps of VAH (resistance zone) from different timeframes could signal a strong ceiling. The multi-timeframe view prevents a trader from, say, going long into a major weekly POC above, or shorting when there’s a huge monthly value-area low just below – situations where awareness of higher timeframe volume structure can make the difference between a good and bad trade.
User Customization: The indicator is flexible in that you can typically adjust which timeframes to include and how many bars to use for each timeframe’s calculation. For example, one might configure it to calculate monthly levels using the past 12 monthly bars (1 year of data), weekly levels using the past 20 weeks, daily using 100 days, etc., depending on preference. By tuning the “bars count” or period length , the trader can focus on recent liquidity zones or incorporate more history if desired. Shorter lookback might catch more recent shifts in volume distribution (important if the market structure changed recently), while longer lookback gives more established levels. This customization ensures the indicator’s output can be tailored to different trading styles (short-term vs swing vs long-term investing). Regardless of settings, the multi-timeframe table allows simultaneous visibility of the chosen timeframes’ volume landscape. This comprehensive view is the core strength: it consolidates data that normally requires flipping through multiple charts.
Using the Liquidity Zones Data for Trading Decisions
Traders can use the information from the MTF Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) indicator in several practical ways to enhance their decision-making:
• Identify Support and Resistance: Each liquidity zone acts as a potential support or resistance area. For example, if the table shows a daily VAH at a certain level above the current price, that level might serve as resistance if the price rallies up to it (since it marks the top of a high-volume region where sellers might step in). Conversely, a weekly VAL below current price could act as support on a dip. By noting these levels in the table, a trader planning an entry or exit can anticipate where the price might stall or reverse. Essentially, you get a map of high-interest price levels from different timeframes, which you can mark on your trading chart for guidance.
• Plan Entries and Exits Around Key Levels: Many traders incorporate volume profile levels into their strategies, for instance: buying near VAL (betting that the value area will hold and price will revert upward), or selling/shorting near VAH (expecting the top of value to hold as resistance), or trading breakouts when price moves outside the value area. With the multi-timeframe table, one can refine these tactics by also considering higher timeframe levels. Suppose you see that on the 1-hour chart the price is just above its 1H POC, but the table indicates that just slightly above, there’s also the daily POC. You might delay a long entry until price clears that daily POC, because that could be a stronger intraday barrier. Or if you intend to take profit on a long trade, you might choose a target just below a weekly VAH since price may struggle to climb past that on the first attempt. The indicator thus acts as a guide for precision in entry/exit decisions, aligning them with where liquidity is high.
• Gauge Trend Strength and Directional Bias: By observing where current price is relative to these volume zones, traders can infer certain market conditions. For instance, if price is trading above the VAH of multiple timeframes’ value areas, it suggests the market is in a more bullish or overextended territory (price accepted above prior value), whereas if price is below multiple VALs, it’s in bearish or undervalued territory relative to recent history. If the price stays around a POC, it indicates consolidation or equilibrium (market comfortable at that price). Traders can use this context for bias – e.g., if price is above the weekly VAH, you might lean bullish but watch for potential pullbacks to that VAH level (now a support). If price is below the monthly VAL, you might avoid longs until it re-enters that value area. In essence, the liquidity zones provide context of value vs. price: is price trading within the high-volume areas (implying range-bound behavior) or outside them (implying a breakout or trending move)? This can prevent chasing trades at poor locations.
• Combine with Other Indicators/Analysis: It’s generally advised to not use any single indicator in isolation, and this holds true here. The liquidity zones from this indicator are best used alongside price action or other technical signals for confirmation . For example, if a bullish candlestick reversal pattern forms right at a confluence of a 4H VAL and Daily POC, that’s a stronger buy signal than the pattern alone. Or if an oscillator shows overbought exactly as price hits a weekly VAH, it adds conviction to a possible short. The indicator’s table basically gives you a shortlist of critical price levels; you can then watch how price behaves at those levels (via candlesticks, order flow, etc.) to make the final trade decision. Traders might set alerts for when price approaches one of the listed levels, or they might drop down to a lower timeframe to fine-tune an entry once a key zone is reached. By integrating this volume-based insight with trend analysis, chart patterns, or momentum indicators, one can make more informed and high-probability decisions rather than trading in the dark.
• Risk Management and Stop Placement: High-liquidity zones can also inform stop-loss placement. Ideally, you want your stop on the other side of a strong support/resistance. If you go long near a VAL, you might place your stop just below the VAL (since a move beyond that suggests the high-volume zone didn’t hold). If you short near a VAH, a stop just above the VAH or POC could be logical. Moreover, if multiple timeframes show overlapping zones, a stop beyond all of them could be even safer (albeit at the cost of a wider stop). The indicator helps identify those spots. It also warns you of where not to put a stop – for example, placing a stop-loss right at a POC might be unwise because price could gravitate to that POC repeatedly (due to its magnetic effect as a high-volume price). Instead, a trader might choose a stop beyond the far side of the value area. By using the table’s information, you can align your risk management with areas of high liquidity, reducing the chance of being whipsawed by normal volatility around heavily traded levels .
Benefits of the Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones Indicator
Using the Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) indicator offers several key benefits for traders, ultimately aiming to streamline analysis and improve decision quality:
• Consolidated Key Levels: It provides a clear, consolidated view of crucial volume-driven levels from multiple timeframes all at once . This saves time and ensures you always account for major support/resistance zones that come from higher or lower timeframe volume clusters. You won’t accidentally overlook a significant weekly level while focused on a 15-minute chart, for example.
• Enhanced Multi-Timeframe Insight: By aligning information from long-term and short-term periods, the indicator helps traders see the “bigger picture” while still operating on their preferred timeframe. This multi-scale awareness can improve trade timing and confidence. You’re effectively doing multi-timeframe analysis with volume profiles in an efficient manner, which can confirm or caution your trade ideas (e.g., a trend looks strong on the 1H, but the table shows a huge monthly VAH just overhead – a reason to be cautious or take profit early).
• Improved Decision Making and Precision: Knowing where liquidity zones lie allows for more precise entries, exits, and stop placements. Traders can make informed decisions such as waiting for a pullback to a value area before entering, or taking profits before price hits a major POC from a higher timeframe. These decisions are grounded in objectively important price levels, potentially leading to higher probability trades and better risk-reward setups. It essentially enhances your strategy by adding a layer of volume context – you’re trading with an awareness of where the market’s interest is heaviest.
• Volume-Based Confirmation: Price alone can sometimes be deceptive, but volume tells the true story of participation. The liquidity zones indicator provides volume-based confirmation of support/resistance. If a price level is identified by this tool, it’s because significant volume happened there – adding weight to that level’s importance. This can help filter out false support/resistance levels that aren’t backed by volume. In other words, it highlights high-quality levels that many traders (and possibly institutions) have shown interest in.
• Adaptable to Different Trading Styles: Whether one is a scalper looking at intraday (15M, 5M charts) or a swing trader focusing on daily/weekly, the indicator can be configured to those needs. You choose which timeframes and how much data to consider. This means the concept of liquidity zones can be applied universally – from spotting intraday pivot levels with volume, to seeing long-term value zones on an investment. The consistent methodology of POC/VAH/VAL across scales provides a common framework to analyze any market and timeframe.
• Informed Risk Management: As discussed, the knowledge of multi-timeframe volume zones aids in risk management. By placing stops beyond major liquidity areas or avoiding trades that run into strong volume walls, traders can reduce the likelihood of whipsaw losses. It’s an extra layer of defense to ensure your trade plan accounts for where the market has historically found lots of interest (hence likely friction). This level of informed planning can be the difference between a well-managed trade and an avoidable loss.
In conclusion, the Multi-Timeframe Liquidity Zones V6 (Table) indicator serves as a powerful analytical aid, giving traders a structured view of where price is likely to encounter support or resistance based on volume concentrations across timeframes. Its functionality centers on identifying those liquidity zones (via POC, VAH, VAL) and presenting them in an easy-to-read format, while its ultimate purpose is to help traders make more informed decisions. By integrating this tool into their workflow, traders can more confidently navigate price action, knowing the objective volume-based landmarks that lie ahead. Remember that while these volume levels often coincide with strong S/R zones, it’s best to use them in conjunction with other technical or fundamental analysis for confirmation . When used appropriately, the indicator can streamline multi-timeframe analysis and enhance your overall trading strategy , giving you an edge in identifying where the market’s liquidity (and opportunity) resides.
Script protetto
Questo script è pubblicato come codice protetto. Tuttavia, è possibile utilizzarle liberamente e senza alcuna limitazione – ulteriori informazioni qui.
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.
Script protetto
Questo script è pubblicato come codice protetto. Tuttavia, è possibile utilizzarle liberamente e senza alcuna limitazione – ulteriori informazioni qui.
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.