OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Aggiornato MACD Enhanced [DCAUT]
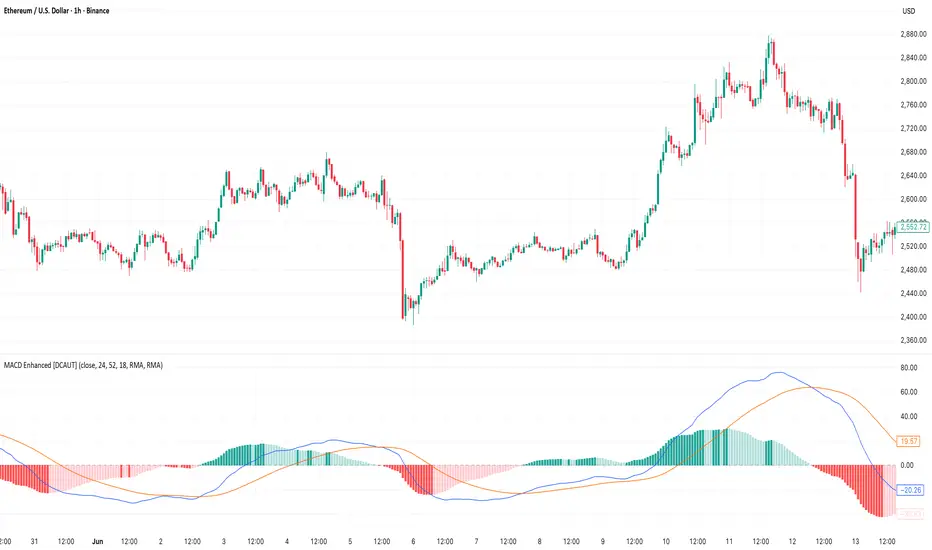
█ MACD Enhanced [DCAUT]
📊 ORIGINALITY & INNOVATION
The MACD Enhanced represents a significant improvement over traditional MACD implementations. While Gerald Appel's original MACD from the 1970s was limited to exponential moving averages (EMA), this enhanced version expands algorithmic options by supporting 21 different moving average calculations for both the main MACD line and signal line independently.
This improvement addresses an important limitation of traditional MACD: the inability to adapt the indicator's mathematical foundation to different market conditions. By allowing traders to select from algorithms ranging from simple moving averages (SMA) for stability to advanced adaptive filters like Kalman Filter for noise reduction, this implementation changes MACD from a fixed-algorithm tool into a flexible instrument that can be adjusted for specific market environments and trading strategies.
The enhanced histogram visualization system uses a four-color gradient that helps communicate momentum strength and direction more clearly than traditional single-color histograms.
📐 MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATION
The core calculation maintains the proven MACD formula: Fast MA(source, fastLength) - Slow MA(source, slowLength), but extends it with algorithmic flexibility. The signal line applies the selected smoothing algorithm to the MACD line over the specified signal period, while the histogram represents the difference between MACD and signal lines.
Available Algorithms:
The implementation supports a comprehensive spectrum of technical analysis algorithms:
Each algorithm responds differently to price action, allowing traders to match the indicator's behavior to market characteristics: trending markets benefit from responsive algorithms like EMA or HMA, while ranging markets require stable algorithms like SMA or RMA.
📊 COMPREHENSIVE SIGNAL ANALYSIS
Histogram Interpretation:
Advanced Signal Recognition:
🎯 STRATEGIC APPLICATIONS
Comprehensive Trend Confirmation Strategies:
Primary Trend Validation Protocol:
Entry Timing Techniques:
Advanced Divergence Trading Systems:
Regular Divergence Recognition:
Hidden Divergence Strategies:
Multi-Timeframe Coordination Framework:
Three-Timeframe Analysis Structure:
Timeframe Synchronization Rules:
Algorithm Considerations by Market Type:
Important Note: All algorithm choices and parameter settings should be thoroughly backtested and validated based on specific trading strategies, market conditions, and individual risk tolerance. Different market environments and trading styles may require different configuration approaches.
📋 DETAILED PARAMETER CONFIGURATION
Comprehensive Source Selection Strategy:
Price Source Analysis and Optimization:
Parameter Configuration Principles:
Important Note: Different moving average algorithms have distinct mathematical characteristics and response patterns. The same parameter settings may produce vastly different results when using different algorithms. When switching algorithms, parameter settings should be re-evaluated and tested for appropriateness.
Length Parameter Considerations:
Comprehensive Algorithm Selection Framework:
MACD Line Algorithm Decision Matrix:
Signal Line Algorithm Optimization Strategies:
Parameter Sensitivity Considerations:
Impact of Parameter Changes:
📈 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS & COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
Response Characteristics by Algorithm:
Noise Filtering Capabilities:
Advanced algorithms like KALMAN_FILTER and SUPER_SMOOTHER help reduce false signals compared to traditional EMA-based MACD. Noise-reducing algorithms can provide more stable signals in volatile market conditions, though results will vary based on market conditions and parameter settings.
Market Condition Adaptability:
Unlike fixed-algorithm MACD, this enhanced version allows real-time optimization. Trending markets benefit from responsive algorithms (EMA, HMA), while ranging markets perform better with stable algorithms (SMA, RMA). The ability to switch algorithms without changing indicators provides greater flexibility.
Comparative Performance vs Traditional MACD:
USAGE NOTES
This indicator is designed for technical analysis and educational purposes. Like all technical indicators, it has limitations and should not be used as the sole basis for trading decisions. Algorithm performance varies with market conditions, and past characteristics do not guarantee future results. Always combine with proper risk management and thorough strategy testing.
📊 ORIGINALITY & INNOVATION
The MACD Enhanced represents a significant improvement over traditional MACD implementations. While Gerald Appel's original MACD from the 1970s was limited to exponential moving averages (EMA), this enhanced version expands algorithmic options by supporting 21 different moving average calculations for both the main MACD line and signal line independently.
This improvement addresses an important limitation of traditional MACD: the inability to adapt the indicator's mathematical foundation to different market conditions. By allowing traders to select from algorithms ranging from simple moving averages (SMA) for stability to advanced adaptive filters like Kalman Filter for noise reduction, this implementation changes MACD from a fixed-algorithm tool into a flexible instrument that can be adjusted for specific market environments and trading strategies.
The enhanced histogram visualization system uses a four-color gradient that helps communicate momentum strength and direction more clearly than traditional single-color histograms.
📐 MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATION
The core calculation maintains the proven MACD formula: Fast MA(source, fastLength) - Slow MA(source, slowLength), but extends it with algorithmic flexibility. The signal line applies the selected smoothing algorithm to the MACD line over the specified signal period, while the histogram represents the difference between MACD and signal lines.
Available Algorithms:
The implementation supports a comprehensive spectrum of technical analysis algorithms:
- Basic Averages: SMA (arithmetic mean), EMA (exponential weighting), RMA (Wilder's smoothing), WMA (linear weighting)
- Advanced Averages: HMA (Hull's low-lag), VWMA (volume-weighted), ALMA (Arnaud Legoux adaptive)
- Mathematical Filters: LSMA (least squares regression), DEMA (double exponential), TEMA (triple exponential), ZLEMA (zero-lag exponential)
- Adaptive Systems: T3 (Tillson T3), FRAMA (fractal adaptive), KAMA (Kaufman adaptive), MCGINLEY_DYNAMIC (reactive to volatility)
- Signal Processing: ULTIMATE_SMOOTHER (low-pass filter), LAGUERRE_FILTER (four-pole IIR), SUPER_SMOOTHER (two-pole Butterworth), KALMAN_FILTER (state-space estimation)
- Specialized: TMA (triangular moving average), LAGUERRE_BINOMIAL_FILTER (binomial smoothing)
Each algorithm responds differently to price action, allowing traders to match the indicator's behavior to market characteristics: trending markets benefit from responsive algorithms like EMA or HMA, while ranging markets require stable algorithms like SMA or RMA.
📊 COMPREHENSIVE SIGNAL ANALYSIS
Histogram Interpretation:
- Positive Values: Indicate bullish momentum when MACD line exceeds signal line, suggesting upward price pressure and potential buying opportunities
- Negative Values: Reflect bearish momentum when MACD line falls below signal line, indicating downward pressure and potential selling opportunities
- Zero Line Crosses: MACD crossing above zero suggests transition to bullish bias, while crossing below indicates bearish bias shift
- Momentum Changes: Rising histogram (regardless of positive/negative) signals accelerating momentum in the current direction, while declining histogram warns of momentum deceleration
Advanced Signal Recognition:
- Divergences: Price making new highs/lows while MACD fails to confirm often precedes trend reversals
- Convergence Patterns: MACD line approaching signal line suggests impending crossover and potential trade setup
- Histogram Peaks: Extreme histogram values often mark momentum exhaustion points and potential reversal zones
🎯 STRATEGIC APPLICATIONS
Comprehensive Trend Confirmation Strategies:
Primary Trend Validation Protocol:
- Identify primary trend direction using higher timeframe (4H or Daily) MACD position relative to zero line
- Confirm trend strength by analyzing histogram progression: consistent expansion indicates strong momentum, contraction suggests weakening
- Use secondary confirmation from MACD line angle: steep angles (>45°) indicate strong trends, shallow angles suggest consolidation
- Validate with price structure: trending markets show consistent higher highs/higher lows (uptrend) or lower highs/lower lows (downtrend)
Entry Timing Techniques:
- Pullback Entries in Uptrends: Wait for MACD histogram to decline toward zero line without crossing, then enter on histogram expansion with MACD line still above zero
- Breakout Confirmations: Use MACD line crossing above zero as confirmation of upward breakouts from consolidation patterns
- Continuation Signals: Look for MACD line re-acceleration (steepening angle) after brief consolidation periods as trend continuation signals
Advanced Divergence Trading Systems:
Regular Divergence Recognition:
- Bullish Regular Divergence: Price creates lower lows while MACD line forms higher lows. This pattern is traditionally considered a potential upward reversal signal, but should be combined with other confirmation signals
- Bearish Regular Divergence: Price makes higher highs while MACD shows lower highs. This pattern is traditionally considered a potential downward reversal signal, but trading decisions should incorporate proper risk management
Hidden Divergence Strategies:
- Bullish Hidden Divergence: Price shows higher lows while MACD displays lower lows, indicating trend continuation potential. Use for adding to existing long positions during pullbacks
- Bearish Hidden Divergence: Price creates lower highs while MACD forms higher highs, suggesting downtrend continuation. Optimal for adding to short positions during bear market rallies
Multi-Timeframe Coordination Framework:
Three-Timeframe Analysis Structure:
- Primary Timeframe (Daily): Determine overall market bias and major trend direction. Only trade in alignment with daily MACD direction
- Secondary Timeframe (4H): Identify intermediate trend changes and major entry opportunities. Use for position sizing decisions
- Execution Timeframe (1H): Precise entry and exit timing. Look for MACD line crossovers that align with higher timeframe bias
Timeframe Synchronization Rules:
- Daily MACD above zero + 4H MACD rising = Strong uptrend context for long positions
- Daily MACD below zero + 4H MACD declining = Strong downtrend context for short positions
- Conflicting signals between timeframes = Wait for alignment or use smaller position sizes
- 1H MACD signals only valid when aligned with both higher timeframes
Algorithm Considerations by Market Type:
- Trending Markets: Responsive algorithms like EMA, HMA may be considered, but effectiveness should be tested for specific market conditions
- Volatile Markets: Noise-reducing algorithms like KALMAN_FILTER, SUPER_SMOOTHER may help reduce false signals, though results vary by market
- Range-Bound Markets: Stability-focused algorithms like SMA, RMA may provide smoother signals, but individual testing is required
- Short Timeframes: Low-lag algorithms like ZLEMA, T3 theoretically respond faster but may also increase noise
Important Note: All algorithm choices and parameter settings should be thoroughly backtested and validated based on specific trading strategies, market conditions, and individual risk tolerance. Different market environments and trading styles may require different configuration approaches.
📋 DETAILED PARAMETER CONFIGURATION
Comprehensive Source Selection Strategy:
Price Source Analysis and Optimization:
- Close Price (Default): Most commonly used, reflects final market sentiment of each period. Best for end-of-day analysis, swing trading, daily/weekly timeframes. Advantages: widely accepted standard, good for backtesting comparisons. Disadvantages: ignores intraday price action, may miss important highs/lows
- HL2 (High+Low)/2: Midpoint of the trading range, reduces impact of opening gaps and closing spikes. Best for volatile markets, gap-prone assets, forex markets. Calculation impact: smoother MACD signals, reduced noise from price spikes. Optimal when asset shows frequent gaps, high volatility during specific sessions
- HLC3 (High+Low+Close)/3: Weighted average emphasizing the close while including range information. Best for balanced analysis, most asset classes, medium-term trading. Mathematical effect: 33% weight to high/low, 33% to close, provides compromise between close and HL2. Use when standard close is too noisy but HL2 is too smooth
- OHLC4 (Open+High+Low+Close)/4: True average of all price points, most comprehensive view. Best for complete price representation, algorithmic trading, statistical analysis. Considerations: includes opening sentiment, smoothest of all options but potentially less responsive. Optimal for markets with significant opening moves, comprehensive trend analysis
Parameter Configuration Principles:
Important Note: Different moving average algorithms have distinct mathematical characteristics and response patterns. The same parameter settings may produce vastly different results when using different algorithms. When switching algorithms, parameter settings should be re-evaluated and tested for appropriateness.
Length Parameter Considerations:
- Fast Length (Default 12): Shorter periods provide faster response but may increase noise and false signals, longer periods offer more stable signals but slower response, different algorithms respond differently to the same parameters and may require adjustment
- Slow Length (Default 26): Should maintain a reasonable proportional relationship with fast length, different timeframes may require different parameter configurations, algorithm characteristics influence optimal length settings
- Signal Length (Default 9): Shorter lengths produce more frequent crossovers but may increase false signals, longer lengths provide better signal confirmation but slower response, should be adjusted based on trading style and chosen algorithm characteristics
Comprehensive Algorithm Selection Framework:
MACD Line Algorithm Decision Matrix:
- EMA (Standard Choice): Mathematical properties: exponential weighting, recent price emphasis. Best for general use, traditional MACD behavior, backtesting compatibility. Performance characteristics: good balance of speed and smoothness, widely understood behavior
- SMA (Stability Focus): Equal weighting of all periods, maximum smoothness. Best for ranging markets, noise reduction, conservative trading. Trade-offs: slower signal generation, reduced sensitivity to recent price changes
- HMA (Speed Optimized): Hull Moving Average, designed for reduced lag. Best for trending markets, quick reversals, active trading. Technical advantage: square root period weighting, faster trend detection. Caution: can be more sensitive to noise
- KAMA (Adaptive): Kaufman Adaptive MA, adjusts smoothing based on market efficiency. Best for varying market conditions, algorithmic trading. Mechanism: fast smoothing in trends, slow smoothing in sideways markets. Complexity: requires understanding of efficiency ratio
Signal Line Algorithm Optimization Strategies:
- Matching Strategy: Use same algorithm for both MACD and signal lines. Benefits: consistent mathematical properties, predictable behavior. Best when backtesting historical strategies, maintaining traditional MACD characteristics
- Contrast Strategy: Use different algorithms for optimization. Common combinations: MACD=EMA, Signal=SMA for smoother crossovers, MACD=HMA, Signal=RMA for balanced speed/stability, Advanced: MACD=KAMA, Signal=T3 for adaptive behavior with smooth signals
- Market Regime Adaptation: Trending markets: both fast algorithms (EMA/HMA), Volatile markets: MACD=KALMAN_FILTER, Signal=SUPER_SMOOTHER, Range-bound: both slow algorithms (SMA/RMA)
Parameter Sensitivity Considerations:
Impact of Parameter Changes:
- Length Parameter Sensitivity: Small parameter adjustments can significantly affect signal timing, while larger adjustments may fundamentally change indicator behavior characteristics
- Algorithm Sensitivity: Different algorithms produce different signal characteristics. Thoroughly test the impact on your trading strategy before switching algorithms
- Combined Effects: Changing multiple parameters simultaneously can create unexpected effects. Recommendation: adjust parameters one at a time and thoroughly test each change
📈 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS & COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
Response Characteristics by Algorithm:
- Fastest Response: ZLEMA, HMA, T3 - minimal lag but higher noise
- Balanced Performance: EMA, DEMA, TEMA - good trade-off between speed and stability
- Highest Stability: SMA, RMA, TMA - reduced noise but increased lag
- Adaptive Behavior: KAMA, FRAMA, MCGINLEY_DYNAMIC - automatically adjust to market conditions
Noise Filtering Capabilities:
Advanced algorithms like KALMAN_FILTER and SUPER_SMOOTHER help reduce false signals compared to traditional EMA-based MACD. Noise-reducing algorithms can provide more stable signals in volatile market conditions, though results will vary based on market conditions and parameter settings.
Market Condition Adaptability:
Unlike fixed-algorithm MACD, this enhanced version allows real-time optimization. Trending markets benefit from responsive algorithms (EMA, HMA), while ranging markets perform better with stable algorithms (SMA, RMA). The ability to switch algorithms without changing indicators provides greater flexibility.
Comparative Performance vs Traditional MACD:
- Algorithm Flexibility: 21 algorithms vs 1 fixed EMA
- Signal Quality: Reduced false signals through noise filtering algorithms
- Market Adaptability: Optimizable for any market condition vs fixed behavior
- Customization Options: Independent algorithm selection for MACD and signal lines vs forced matching
- Professional Features: Advanced color coding, multiple alert conditions, comprehensive parameter control
USAGE NOTES
This indicator is designed for technical analysis and educational purposes. Like all technical indicators, it has limitations and should not be used as the sole basis for trading decisions. Algorithm performance varies with market conditions, and past characteristics do not guarantee future results. Always combine with proper risk management and thorough strategy testing.
Note di rilascio
v2 (2025.10.14)- Changed default parameters from 12/26/9 (EMA) to 24/52/18 (RMA)
- Optimized for major trend identification in medium to long-term trading
- Better suited for high-volatility markets (crypto, forex, volatile stocks)
- For short-term trading, consider using traditional values (12/26/9 with EMA)
Script open-source
Nello spirito di TradingView, l'autore di questo script lo ha reso open source, in modo che i trader possano esaminarne e verificarne la funzionalità. Complimenti all'autore! Sebbene sia possibile utilizzarlo gratuitamente, ricordiamo che la ripubblicazione del codice è soggetta al nostro Regolamento.
DCAUT is a professional automated bot platform. While we share indicators here for research, our ecosystem offers intelligent algorithmic solutions. Deploy advanced bots for seamless 24/7 execution.
🌐 dcaut.com
🌐 dcaut.com
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.
Script open-source
Nello spirito di TradingView, l'autore di questo script lo ha reso open source, in modo che i trader possano esaminarne e verificarne la funzionalità. Complimenti all'autore! Sebbene sia possibile utilizzarlo gratuitamente, ricordiamo che la ripubblicazione del codice è soggetta al nostro Regolamento.
DCAUT is a professional automated bot platform. While we share indicators here for research, our ecosystem offers intelligent algorithmic solutions. Deploy advanced bots for seamless 24/7 execution.
🌐 dcaut.com
🌐 dcaut.com
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.