OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Aggiornato VWAP Separation Oscillator V5 (No Arrows)
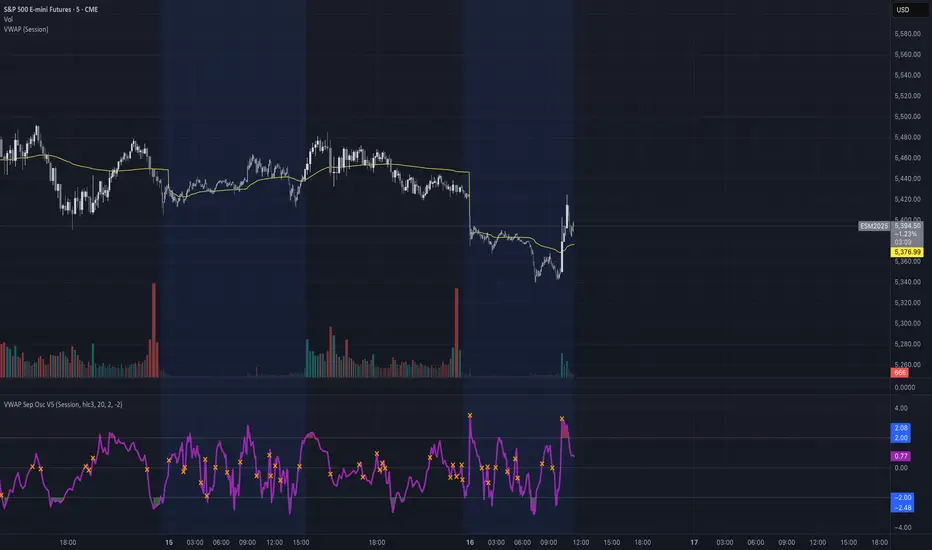
Okay, here is a draft description you can adapt for your TradingView publication. It starts from the basics and explains the concepts behind the indicator and how to interpret its visual elements.
VWAP Separation Oscillator [Z-Score]
Summary
This indicator provides a normalized view of how far the current price has deviated from its Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP), helping traders identify potentially overbought or oversold conditions relative to recent VWAP dynamics. It calculates the price separation from VWAP and expresses it in terms of standard deviations (a Z-score), making it easier to gauge the statistical significance of the deviation.
Core Concepts Explained
What is VWAP?
What is VWAP Separation?
P
How Standard Deviation is Used:
The Oscillator Line (Z-Score):
Visual Elements Explained
Potential Usage / Interpretation
Context is Key: This oscillator measures deviation from a specific benchmark (VWAP). Its interpretation should always be done within the context of the overall market trend, price structure (support/resistance), volume analysis, and potentially other confirming indicators.
Disclaimer: This indicator is a tool for analysis, not a standalone trading system. It does not provide financial advice. Always use risk management.
Settings Overview
VWAP Separation Oscillator [Z-Score]
Summary
This indicator provides a normalized view of how far the current price has deviated from its Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP), helping traders identify potentially overbought or oversold conditions relative to recent VWAP dynamics. It calculates the price separation from VWAP and expresses it in terms of standard deviations (a Z-score), making it easier to gauge the statistical significance of the deviation.
Core Concepts Explained
What is VWAP?
- VWAP stands for Volume-Weighted Average Price. It's a trading benchmark calculated by taking the total dollar value traded for every transaction (price multiplied by volume) and dividing it by the total shares traded for the day (or other chosen period).
- Unlike a simple moving average, VWAP gives more weight to price levels where more volume occurred. Many institutional traders use it as a reference point for execution quality.
- This indicator allows you to choose the "Anchor Period" (Session, Week, Month, etc.) which determines when the VWAP calculation resets.
What is VWAP Separation?
P
- rice doesn't always stay at the VWAP; it naturally fluctuates above and below it.
- "VWAP Separation" is simply the difference between the current price (Source) and the calculated VWAP value (Separation = Price - VWAP). A positive separation means the price is above VWAP; negative means below.
How Standard Deviation is Used:
- While knowing the separation is useful, its significance can vary wildly between different stocks or market conditions. A $1 separation might be huge for one stock but tiny for another.
- Standard Deviation is a statistical measure of how spread out data points are from their average. In this indicator, we calculate the standard deviation of the VWAP Separation over a specified Lookback Length. This tells us how volatile or dispersed the separation has been recently.
The Oscillator Line (Z-Score):
- The main purple (or Green/Red) line plotted by this indicator is the Z-score of the VWAP Separation.
- Formula conceptually: Oscillator Value = (Current Separation - Average Separation) / Standard Deviation of Separation
- Interpretation: It tells you how many standard deviations the current separation is away from the average separation over the lookback period.
- A value of +2.0 means the current separation is 2 standard deviations higher (more extended to the upside) than the average separation.
- A value of -1.5 means the current separation is 1.5 standard deviations lower (more extended to the downside) than the average separation.
- This normalization makes it easier to compare readings across different assets or timeframes and to define consistent thresholds for "extreme" deviations.
Visual Elements Explained
- Oscillator Line: The primary line showing the Z-score value (explained above). Can optionally be colored Green/Red based on its slope (rising/falling).
- Overbought Line (Solid Red): A user-defined level (default: 2.0). When the oscillator moves above this line, it suggests the price deviation above VWAP is statistically significant compared to recent history.
- Oversold Line (Solid Green): A user-defined level (default: -2.0). When the oscillator moves below this line, it suggests the price deviation below VWAP is statistically significant compared to recent history.
- Overbought/Oversold Zone Fills (Transparent Red/Green): These shaded areas appear only when the oscillator line enters the respective Overbought or Oversold territory (defined by the OB/OS Lines), visually highlighting these periods.
- Zero Line (Dotted Gray): Represents the point where the current VWAP separation is exactly equal to the average VWAP separation over the lookback period. Crossings indicate shifts relative to this mean.
- Zero Cross Markers (Orange 'X'): Small 'x' marks plotted directly on the oscillator line whenever it crosses the Zero Line, pinpointing these moments.
Potential Usage / Interpretation
- Identifying Extremes: High positive values (above OB Level) or low negative values (below OS Level) can suggest the price move relative to VWAP might be over-extended and potentially due for a pause or pullback. Look for the oscillator turning back from these extremes.
- Spotting Divergences: Look for discrepancies between price action and the oscillator.
- Bearish Divergence: Price makes a new high, but the oscillator makes a lower high (often in the OB zone). Suggests weakening upside momentum relative to VWAP dynamics.
- Bullish Divergence: Price makes a new low, but the oscillator makes a higher low (often in the OS zone). Suggests weakening downside momentum relative to VWAP dynamics.
Context is Key: This oscillator measures deviation from a specific benchmark (VWAP). Its interpretation should always be done within the context of the overall market trend, price structure (support/resistance), volume analysis, and potentially other confirming indicators.
Disclaimer: This indicator is a tool for analysis, not a standalone trading system. It does not provide financial advice. Always use risk management.
Settings Overview
- Anchor Period: Determines how often the VWAP calculation resets (Session, Week, Month, etc.).
- Source: The price data used for the separation calculation (default: hlc3).
- Lookback Length: The number of bars used to calculate the average and standard deviation of the separation, influencing the oscillator's responsiveness.
- Overbought/Oversold Levels: User-defined thresholds for identifying extreme Z-score values.
- Color Oscillator Line: Option to color the oscillator line based on whether it's rising or falling.
Note di rilascio
VWAP Separation Oscillator [Z-Score]Summary
This indicator provides a normalized view of how far the current price has deviated from its Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP), helping traders identify potentially overbought or oversold conditions relative to recent VWAP dynamics. It calculates the price separation from VWAP and expresses it in terms of standard deviations (a Z-score), making it easier to gauge the statistical significance of the deviation.
Core Concepts Explained
What is VWAP?
- VWAP stands for Volume-Weighted Average Price. It's a trading benchmark calculated by taking the total dollar value traded for every transaction (price multiplied by volume) and dividing it by the total shares traded for the day (or other chosen period).
- Unlike a simple moving average, VWAP gives more weight to price levels where more volume occurred. Many institutional traders use it as a reference point for execution quality.
- This indicator allows you to choose the "Anchor Period" (Session, Week, Month, etc.) which determines when the VWAP calculation resets.
What is VWAP Separation?
- Price doesn't always stay at the VWAP; it naturally fluctuates above and below it.
- "VWAP Separation" is simply the difference between the current price (Source) and the calculated VWAP value (Separation = Price - VWAP). A positive separation means the price is above VWAP; negative means below
How Standard Deviation is Used:
- While knowing the separation is useful, its significance can vary wildly between different stocks or market conditions. A $1 separation might be huge for one stock but tiny for another.
- Standard Deviation is a statistical measure of how spread out data points are from their average. In this indicator, we calculate the standard deviation of the VWAP Separation over a specified Lookback Length. This tells us how volatile or dispersed the separation has been recently.
The Oscillator Line (Z-Score):
- The main purple (or Green/Red) line plotted by this indicator is the Z-score of the VWAP Separation.
- Formula conceptually: Oscillator Value = (Current Separation - Average Separation) / Standard Deviation of Separation
- Interpretation: It tells you how many standard deviations the current separation is away from the average separation over the lookback period.
- A value of +2.0 means the current separation is 2 standard deviations higher (more extended to the upside) than the average separation.
- A value of -1.5 means the current separation is 1.5 standard deviations lower (more extended to the downside) than the average separation.
- This normalization makes it easier to compare readings across different assets or timeframes and to define consistent thresholds for "extreme" deviations.
Visual Elements Explained
- Oscillator Line: The primary line showing the Z-score value (explained above). Can optionally be colored Green/Red based on its slope (rising/falling).
- Overbought Line (Solid Red): A user-defined level (default: 2.0). When the oscillator moves above this line, it suggests the price deviation above VWAP is statistically significant compared to recent history.
- Oversold Line (Solid Green): A user-defined level (default: -2.0). When the oscillator moves below this line, it suggests the price deviation below VWAP is statistically significant compared to recent history.
- Overbought/Oversold Zone Fills (Transparent Red/Green): These shaded areas appear only when the oscillator line enters the respective Overbought or Oversold territory (defined by the OB/OS Lines), visually highlighting these periods.
- Zero Line (Dotted Gray): Represents the point where the current VWAP separation is exactly equal to the average VWAP separation over the lookback period. Crossings indicate shifts relative to this mean.
- Zero Cross Markers (Orange 'X'): Small 'x' marks plotted directly on the oscillator line whenever it crosses the Zero Line, pinpointing these moments.
Potential Usage / Interpretation
- Identifying Extremes: High positive values (above OB Level) or low negative values (below OS Level) can suggest the price move relative to VWAP might be over-extended and potentially due for a pause or pullback. Look for the oscillator turning back from these extremes.
- Spotting Divergences: Look for discrepancies between price action and the oscillator.
- Bearish Divergence: Price makes a new high, but the oscillator makes a lower high (often in the OB zone). Suggests weakening upside momentum relative to VWAP dynamics.
- Bullish Divergence: Price makes a new low, but the oscillator makes a higher low (often in the OS zone). Suggests weakening downside momentum relative to VWAP dynamics.
- Context is Key: This oscillator measures deviation from a specific benchmark (VWAP). Its interpretation should always be done within the context of the overall market trend, price structure (support/resistance), volume analysis, and potentially other confirming indicators.
- Disclaimer: This indicator is a tool for analysis, not a standalone trading system. It does not provide financial advice. Always use risk management.
Settings Overview
- Anchor Period: Determines how often the VWAP calculation resets (Session, Week, Month, etc.).
- Source: The price data used for the separation calculation (default: hlc3).
- Lookback Length: The number of bars used to calculate the average and standard deviation of the separation, influencing the oscillator's responsiveness.
- Overbought/Oversold Levels: User-defined thresholds for identifying extreme Z-score values.
- Color Oscillator Line: Option to color the oscillator line based on whether it's rising or falling.
Script open-source
Nello spirito di TradingView, l'autore di questo script lo ha reso open source, in modo che i trader possano esaminarne e verificarne la funzionalità. Complimenti all'autore! Sebbene sia possibile utilizzarlo gratuitamente, ricordiamo che la ripubblicazione del codice è soggetta al nostro Regolamento.
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.
Script open-source
Nello spirito di TradingView, l'autore di questo script lo ha reso open source, in modo che i trader possano esaminarne e verificarne la funzionalità. Complimenti all'autore! Sebbene sia possibile utilizzarlo gratuitamente, ricordiamo che la ripubblicazione del codice è soggetta al nostro Regolamento.
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.