OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Pasrsifal.RegressionTrendState
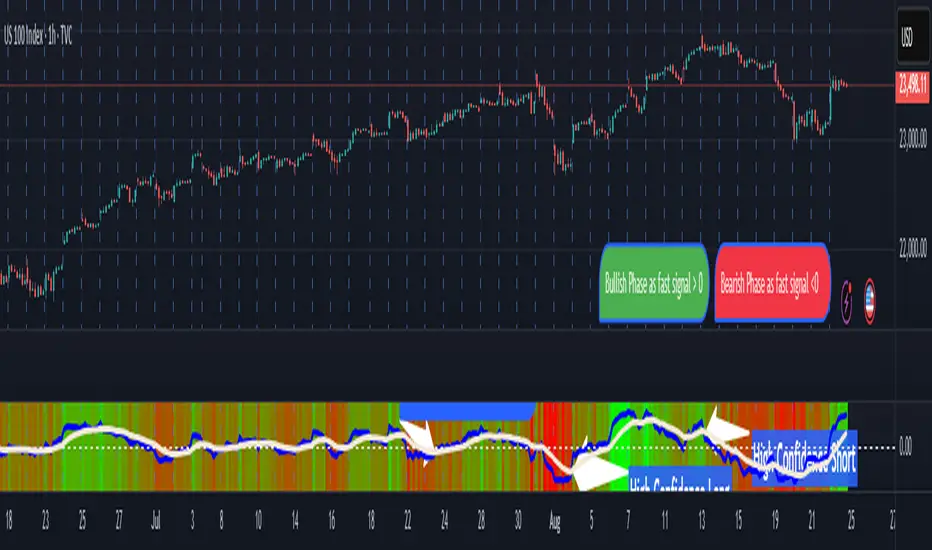
Summary
The Parsifal.Regression.Trend.State Indicator analyzes the leading coefficients of linear and quadratic regressions of price (against time). It also considers their first- and second-order changes. These features are aggregated into a Trend-State background, shown as a gradient color. In addition, the indicator generates fast and slow signals that can be used as potential entry- or exit triggers.
This tool is designed for advanced trend-following strategies, leveraging information from multiple trendline features.
Background
Trendlines provide insight into the state of a trend or the “trendiness” of a price process. While moving averages or pivot-based lines can serve as envelopes and breakout levels, they are often too lagging for swing traders, who need tools that adapt more closely to price swings, ideally using trendlines, around which the price process swings continuously.
Regression lines address this by cutting directly through the data, making them a natural anchor for observing how price winds around a central trendline within a chosen lookback period.
Regression Trendlines
• Linear Regression:
o Minimizes distance to all closing values over the lookback period.
o The slope represents the short-term linear trend.
o The change of slope indicates trend acceleration or deceleration.
o Linear regression lags during phases of rapid market shifts.
• Quadratic Regression:
o Fits a second-degree polynomial to minimize deviation from closing prices.
o The convexity term (leading coefficient) reflects curvature:
Positive convexity → accelerating uptrend or fading downtrend.
Negative convexity → accelerating downtrend or fading uptrend.
o The change of convexity detects early shifts in momentum and often reacts faster than slope features.
Features Extracted
The indicator evaluates six features:
• Linear features: slope, first derivative of slope, second derivative of slope.
• Quadratic features: convexity term, first derivative of the convexity term, second derivative of the convexity term.
• Linear features: capture broad, background trend behavior.
• Quadratic features: detect deviations, accelerations, and smaller-scale dynamics.
Quadratic terms generally react first to market changes, while linear terms provide stability and context.
Dynamics of Market Moves as seen by linear and quadratic regressions
• At the start of a rapid move:
The change of convexity reacts first, capturing the shift in dynamics before other features. The convexity term then follows, while linear slope features lag further behind. Because convexity measures deviation from linearity, it reflects accelerating momentum more effectively than slope.
• At the end of a rapid move:
Again, the change of convexity responds first to fading momentum, signaling the transition from above-linear to below-linear dynamics. Even while a strong trend persists, the change of convexity may flip sign early, offering a warning of weakening strength. The convexity term itself adjusts more slowly but may still turn before the price process does. Linear features lag the most, typically only flipping after price has already reversed, thereby smoothing out the rapid, more sensitive reactions of quadratic terms.
________________________________________
Parsifal Regression.Trend.State Method
1. Feature Mapping:
Each feature is mapped to a range between -1 and 1, preserving zero-crossings (critical for sign interpretation).
2. Aggregation:
A heuristic linear combination*) produces a background information value, visualized as a gradient color scale:
o Deep green → strong positive trend.
o Deep red → strong negative trend.
o Yellow → neutral or transitional states.
3. Signals:
o Fast signal (oscillator): ranges from -1 to 1, reflecting short-term trend state.
o Slow signal (smoothed): moving average of the fast signal.
o Their interactions (crossovers, zero-crossings) provide actionable trading triggers.
How to Use
The Trend-State background gradient provides intuitive visual feedback on the aggregated regression features (slope, convexity, and their changes). Because these features reflect not only current trend strength but also their acceleration or deceleration, the color transitions help anticipate evolving market states:
• Solid Green: All features near their highs. Indicates a strong, accelerating uptrend. May also reflect explosive or hyperbolic upside moves (including gaps).
• Fading Solid Green: A recently strong uptrend is losing momentum. Price may shift into a slower uptrend, consolidation, or even a reversal.
• Fading Green → Yellow: Often appears as a dirty yellow or a rapidly mixing pattern of green and red. Signals that the uptrend is weakening toward neutrality or beginning to turn negative.
• Yellow → Deepening Red: Two possible scenarios:
o Coming from a strong uptrend → suggests a sharp fade, though the trend may still technically be up.
o Coming from a weaker uptrend or sideways market → suggests the start of an accelerating downtrend.
• Solid Red: All features near their lows. Indicates a strong, accelerating downtrend. May also reflect crash-type conditions or downside gaps.
• Fading Solid Red: A recently strong downtrend is losing strength. Market may move into a slower decline, consolidation, or early reversal upward.
• Fading Red → Yellow: The downtrend is weakening toward neutral, with potential for a bullish shift.
• Yellow → Increasing Green: Two possible scenarios:
o Coming from a strong downtrend, it reflects a sharp fade of bearish momentum, though the market may still technically be trending down.
o Coming from a weaker downtrend or sideways movement, it suggests the start of an accelerating uptrend.
Note: Market evolution does not always follow this neat “color cycle.” It may jump between states, skip stages, or reverse abruptly depending on market conditions. This makes the background coloring particularly valuable as a contextual map of current and evolving price dynamics.
Signal Crossovers:
Although the fast signal is very similar (but not identical) to the background coloring, it provides a numerical representation indicating a bullish interpretation for rising values and bearish for falling.
o High-confidence entries:
Fast signal rising from < -0.7 and crossing above the slow signal → potential long entry.
Fast signal falling from > +0.7 and crossing below the slow signal → potential short entry.
o Low-confidence entries:
Crossovers near zero may still provide a valid trigger but may be noisy and should be confirmed with other signals.
o Zero-crossings:
Indicate broader state changes, useful for conservative positioning or option strategies. For confirmation of a Fast signal 0-crossing, wait for the Slow signal to cross as well.
________________________________________
*) Note on Aggregation
While the indicator currently uses a heuristic linear combination of features, alternatives such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) could provide a more formal aggregation. However, while in the absence of matrix algebra, the required eigenvalue decomposition can be approximated, its computational expense does not justify the marginal higher insight in this case. The current heuristic approach offers a practical balance of clarity, speed, and accuracy.
The Parsifal.Regression.Trend.State Indicator analyzes the leading coefficients of linear and quadratic regressions of price (against time). It also considers their first- and second-order changes. These features are aggregated into a Trend-State background, shown as a gradient color. In addition, the indicator generates fast and slow signals that can be used as potential entry- or exit triggers.
This tool is designed for advanced trend-following strategies, leveraging information from multiple trendline features.
Background
Trendlines provide insight into the state of a trend or the “trendiness” of a price process. While moving averages or pivot-based lines can serve as envelopes and breakout levels, they are often too lagging for swing traders, who need tools that adapt more closely to price swings, ideally using trendlines, around which the price process swings continuously.
Regression lines address this by cutting directly through the data, making them a natural anchor for observing how price winds around a central trendline within a chosen lookback period.
Regression Trendlines
• Linear Regression:
o Minimizes distance to all closing values over the lookback period.
o The slope represents the short-term linear trend.
o The change of slope indicates trend acceleration or deceleration.
o Linear regression lags during phases of rapid market shifts.
• Quadratic Regression:
o Fits a second-degree polynomial to minimize deviation from closing prices.
o The convexity term (leading coefficient) reflects curvature:
Positive convexity → accelerating uptrend or fading downtrend.
Negative convexity → accelerating downtrend or fading uptrend.
o The change of convexity detects early shifts in momentum and often reacts faster than slope features.
Features Extracted
The indicator evaluates six features:
• Linear features: slope, first derivative of slope, second derivative of slope.
• Quadratic features: convexity term, first derivative of the convexity term, second derivative of the convexity term.
• Linear features: capture broad, background trend behavior.
• Quadratic features: detect deviations, accelerations, and smaller-scale dynamics.
Quadratic terms generally react first to market changes, while linear terms provide stability and context.
Dynamics of Market Moves as seen by linear and quadratic regressions
• At the start of a rapid move:
The change of convexity reacts first, capturing the shift in dynamics before other features. The convexity term then follows, while linear slope features lag further behind. Because convexity measures deviation from linearity, it reflects accelerating momentum more effectively than slope.
• At the end of a rapid move:
Again, the change of convexity responds first to fading momentum, signaling the transition from above-linear to below-linear dynamics. Even while a strong trend persists, the change of convexity may flip sign early, offering a warning of weakening strength. The convexity term itself adjusts more slowly but may still turn before the price process does. Linear features lag the most, typically only flipping after price has already reversed, thereby smoothing out the rapid, more sensitive reactions of quadratic terms.
________________________________________
Parsifal Regression.Trend.State Method
1. Feature Mapping:
Each feature is mapped to a range between -1 and 1, preserving zero-crossings (critical for sign interpretation).
2. Aggregation:
A heuristic linear combination*) produces a background information value, visualized as a gradient color scale:
o Deep green → strong positive trend.
o Deep red → strong negative trend.
o Yellow → neutral or transitional states.
3. Signals:
o Fast signal (oscillator): ranges from -1 to 1, reflecting short-term trend state.
o Slow signal (smoothed): moving average of the fast signal.
o Their interactions (crossovers, zero-crossings) provide actionable trading triggers.
How to Use
The Trend-State background gradient provides intuitive visual feedback on the aggregated regression features (slope, convexity, and their changes). Because these features reflect not only current trend strength but also their acceleration or deceleration, the color transitions help anticipate evolving market states:
• Solid Green: All features near their highs. Indicates a strong, accelerating uptrend. May also reflect explosive or hyperbolic upside moves (including gaps).
• Fading Solid Green: A recently strong uptrend is losing momentum. Price may shift into a slower uptrend, consolidation, or even a reversal.
• Fading Green → Yellow: Often appears as a dirty yellow or a rapidly mixing pattern of green and red. Signals that the uptrend is weakening toward neutrality or beginning to turn negative.
• Yellow → Deepening Red: Two possible scenarios:
o Coming from a strong uptrend → suggests a sharp fade, though the trend may still technically be up.
o Coming from a weaker uptrend or sideways market → suggests the start of an accelerating downtrend.
• Solid Red: All features near their lows. Indicates a strong, accelerating downtrend. May also reflect crash-type conditions or downside gaps.
• Fading Solid Red: A recently strong downtrend is losing strength. Market may move into a slower decline, consolidation, or early reversal upward.
• Fading Red → Yellow: The downtrend is weakening toward neutral, with potential for a bullish shift.
• Yellow → Increasing Green: Two possible scenarios:
o Coming from a strong downtrend, it reflects a sharp fade of bearish momentum, though the market may still technically be trending down.
o Coming from a weaker downtrend or sideways movement, it suggests the start of an accelerating uptrend.
Note: Market evolution does not always follow this neat “color cycle.” It may jump between states, skip stages, or reverse abruptly depending on market conditions. This makes the background coloring particularly valuable as a contextual map of current and evolving price dynamics.
Signal Crossovers:
Although the fast signal is very similar (but not identical) to the background coloring, it provides a numerical representation indicating a bullish interpretation for rising values and bearish for falling.
o High-confidence entries:
Fast signal rising from < -0.7 and crossing above the slow signal → potential long entry.
Fast signal falling from > +0.7 and crossing below the slow signal → potential short entry.
o Low-confidence entries:
Crossovers near zero may still provide a valid trigger but may be noisy and should be confirmed with other signals.
o Zero-crossings:
Indicate broader state changes, useful for conservative positioning or option strategies. For confirmation of a Fast signal 0-crossing, wait for the Slow signal to cross as well.
________________________________________
*) Note on Aggregation
While the indicator currently uses a heuristic linear combination of features, alternatives such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) could provide a more formal aggregation. However, while in the absence of matrix algebra, the required eigenvalue decomposition can be approximated, its computational expense does not justify the marginal higher insight in this case. The current heuristic approach offers a practical balance of clarity, speed, and accuracy.
Script open-source
Nello spirito di TradingView, l'autore di questo script lo ha reso open source, in modo che i trader possano esaminarne e verificarne la funzionalità. Complimenti all'autore! Sebbene sia possibile utilizzarlo gratuitamente, ricordiamo che la ripubblicazione del codice è soggetta al nostro Regolamento.
parsifaltrading
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.
Script open-source
Nello spirito di TradingView, l'autore di questo script lo ha reso open source, in modo che i trader possano esaminarne e verificarne la funzionalità. Complimenti all'autore! Sebbene sia possibile utilizzarlo gratuitamente, ricordiamo che la ripubblicazione del codice è soggetta al nostro Regolamento.
parsifaltrading
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.