OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Old Price Oscillator
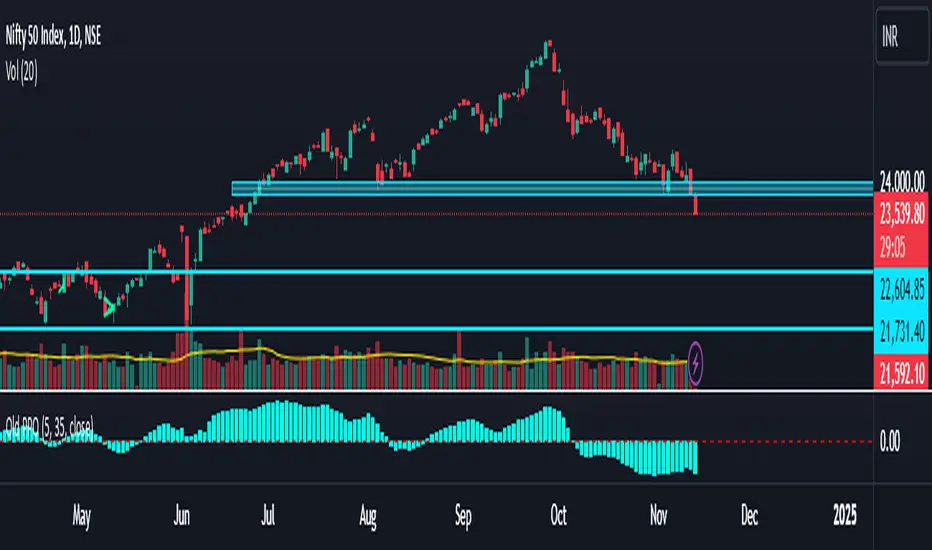
The Old Price Oscillator (OPO) is a momentum indicator widely used by traders and analysts to gauge the direction and strength of price trends. It works by calculating the difference between two moving averages—a shorter-term moving average and a longer-term moving average—of a security’s price. This difference is plotted as an oscillating line, helping traders visualize the momentum and determine when price reversals or continuations might occur. Typically, when the oscillator value is positive, the price is trending upwards, suggesting potential buy signals; conversely, when the oscillator turns negative, it indicates downward momentum, which could signal a potential sell.
The OPO is similar to other oscillators, like the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), in that it uses moving averages to smooth out price fluctuations and clarify trends. Traders often customize the length of the short- and long-term moving averages to better suit specific assets or market conditions. Generally, this indicator is especially useful in markets that exhibit clear trends. However, it may generate false signals during sideways or highly volatile periods, so many traders combine the OPO with other technical indicators or filters to improve accuracy.
The OPO is similar to other oscillators, like the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), in that it uses moving averages to smooth out price fluctuations and clarify trends. Traders often customize the length of the short- and long-term moving averages to better suit specific assets or market conditions. Generally, this indicator is especially useful in markets that exhibit clear trends. However, it may generate false signals during sideways or highly volatile periods, so many traders combine the OPO with other technical indicators or filters to improve accuracy.
Script open-source
Nello spirito di TradingView, l'autore di questo script lo ha reso open source, in modo che i trader possano esaminarne e verificarne la funzionalità. Complimenti all'autore! Sebbene sia possibile utilizzarlo gratuitamente, ricordiamo che la ripubblicazione del codice è soggetta al nostro Regolamento.
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.
Script open-source
Nello spirito di TradingView, l'autore di questo script lo ha reso open source, in modo che i trader possano esaminarne e verificarne la funzionalità. Complimenti all'autore! Sebbene sia possibile utilizzarlo gratuitamente, ricordiamo che la ripubblicazione del codice è soggetta al nostro Regolamento.
Declinazione di responsabilità
Le informazioni e le pubblicazioni non sono intese come, e non costituiscono, consulenza o raccomandazioni finanziarie, di investimento, di trading o di altro tipo fornite o approvate da TradingView. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare i Termini di utilizzo.